View Satisfaction Model
Simulating human perception with ML
- Authors: Jaeha Kim, Michael Kent, Katharina Kral, Timur Dogan
- Date: 2021 - Ongoing
People spend approximately 90% of their lives indoors, and thus arguably, the design of these spaces can significantly influence occupant well-being. Adequate views to the outside are one of the most cited indoor qualities related to occupant well-being. Analyzing view quality is becoming increasingly important as indoor spaces with vistas and views to the outside are becoming a rare commodity due to urbanization and densification trends. However, to better understand occupant view satisfaction and provide more reliable design feedback to architects, existing view satisfaction rating data must be expanded to capture a wider variety of view scenarios and occupants. In addition, most research on occupant view satisfaction remains challenging in practice due to a lack of easy-to-use early-design analysis tools. However, early assessment of view quality can be advantageous as design decisions in early design, such as building orientation, floorplan layout, and façade design, can make or break the view quality.
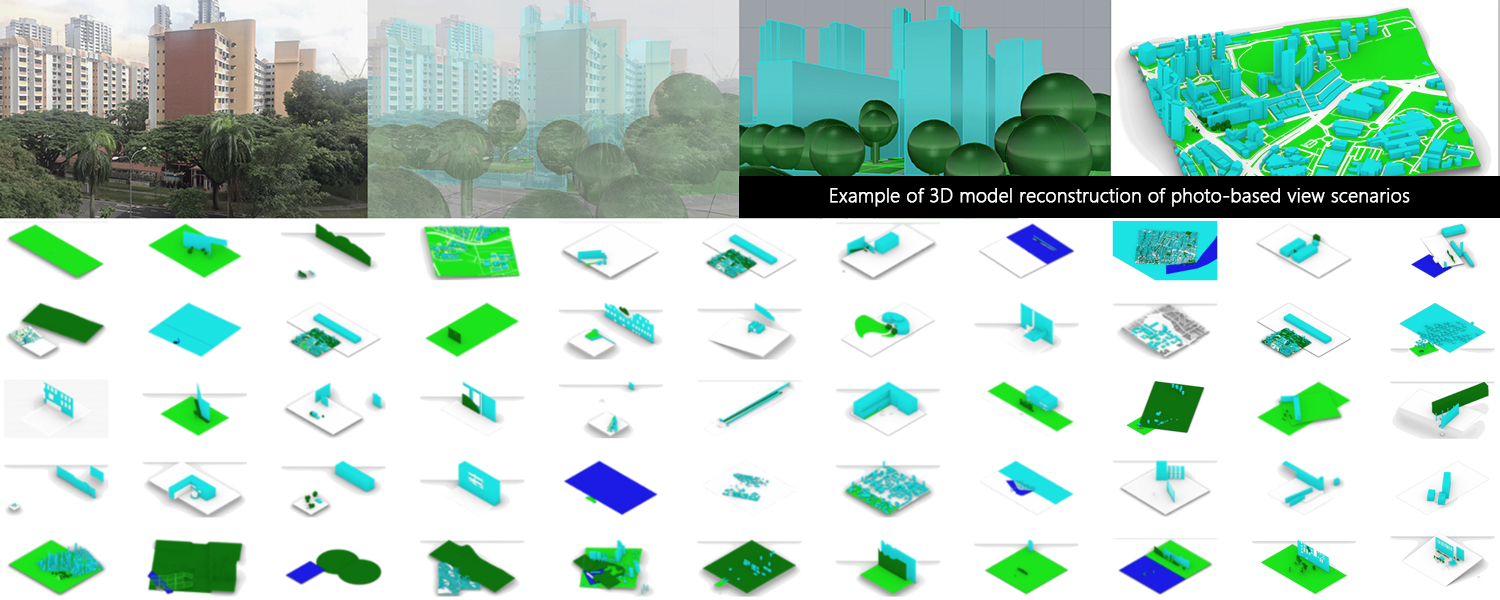
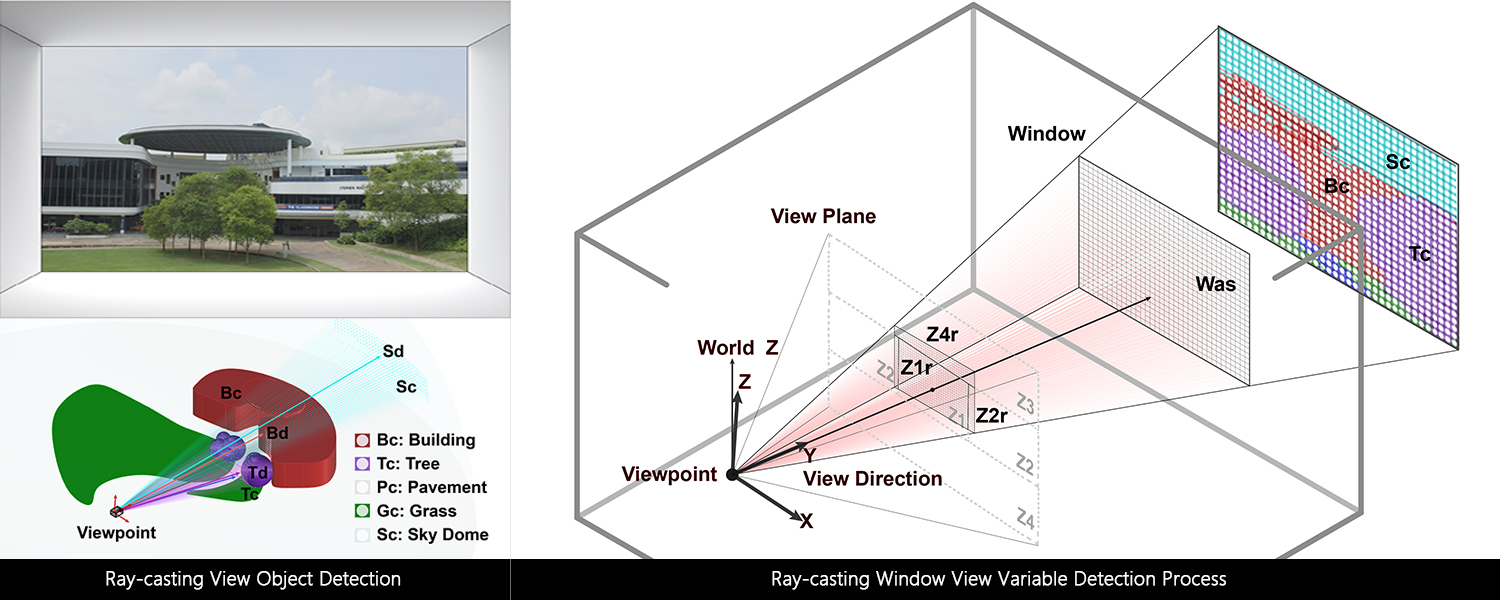
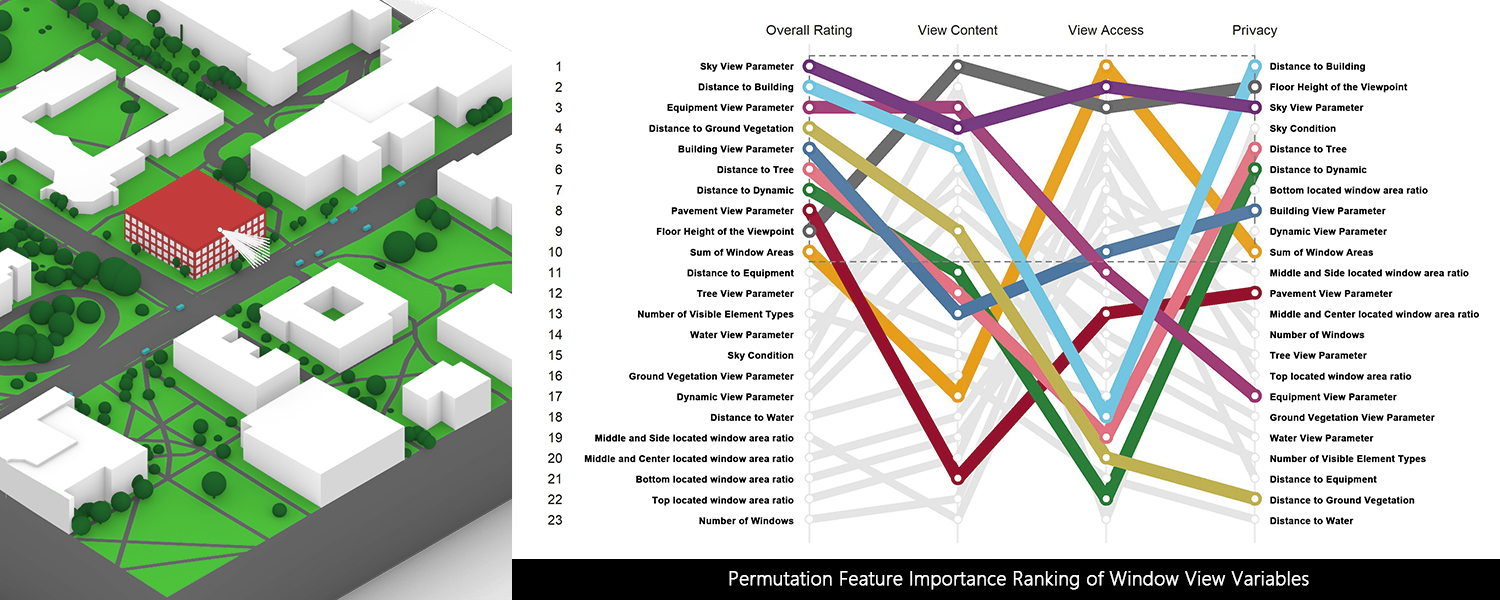
This paper, hence, presents results from a 181 participant online view satisfaction survey with 590 unique window view scenarios. The data collected from this survey is used to train a tree-regression model to predict occupant view satisfaction. The prediction performance was compared to an existing window view assessment framework through case studies. The result showed that the new prediction (MAE = 0.53, RMSE = 0.65) is more accurate to the surveyed satisfaction result than the existing framework (MAE = 3.66, RMSE = 3.78) with lower mean absolute error and root mean squared error. Further, the new prediction performance was generally high (R2 ≥ 0.64) for most surveyed responses collected, verifying the reliability of the prediction. To facilitate wider use of view analysis in early design, this paper also describes integrating the view satisfaction prediction model and a ray-casting tool to compute view parameters from a 3D model into the popular Rhino CAD environment.